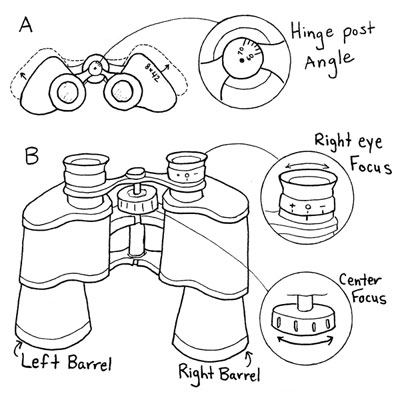
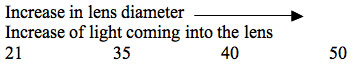Home | About Us | How to Participate | Biodiversity Modules | Projects | Maps | News | Resources NatureMapping Activities4: Using Binoculars/Monoculars.Purpose: Materials Needed:
Teacher’s Guide:
Teachers Notes:
Predator & Prey Importance of magnification, light-gathering power, stereoscopic and monocular vision to predators and prey. Some birds of prey have stereoscopic vision - they use both eyes to focus on prey. Peregrine falcons eyeballs change shape when they are closing in at almost 200 mph after prey. Eagles can see prey almost 2 miles away. The lens in their eyes have high magnification powers, just like the binoculars the Coast Guard uses to read ship names very far away. Another bird of prey, the owl, finds its prey in the dark. It needs light-gathering power more than magnification to be successful. Owl eyes are very large, gathering much light Pigeons and other prey species need a large field of vision in order to watch for predators. Their eyes are placed on either side of their head. Pigeon eyes are monocular. Each eye can focus independent of the other eye. Prey animals often stay in large groups so there are more eyes watching for predators. Prey animals have survival techniques that allow them to escape if caught. The pigeon has quick release feathers. Unless a Peregrine falcon has a good grip on the body of a pigeon it will have a bunch of feathers in its talons and the pigeon will escape.
The larger diameter allows a greater amount of light to enter. The diameter of the lens refers to the Field of Vision. Click on picture to see effect of a change in lens diameter..
Magnification


Using a higher magnification (10x) you can identify birds from a distance. Field of ViewWide Angle vs. Standard Lens 

Using a wide angle lens (left), you can see more in the field of view than with a standard lens (right). The wide angle lens makes it easier to scan for wildlife in the field.
No Student Guide DefinitionsBinoculars - an optical instrument with a separate lens for each eye, used for viewing distant objects. Habitat - the type of environment in which an organism or group normally lives Magnification - the ratio of the size of an image to the size of the object Monocular vision - vision with only one eye Stereoscopic vision - three-dimensional vision produced by the fusion of two slightly different views of a scene on each retina Talons - the sharp nails on the foot of a bird which it uses when hunting animals |